Guide to colocation and how to choose a provider
It's important to thoroughly evaluate facilities, pricing and contract terms before choosing a colocation provider. Also, consider the challenges that come with going colo.
A data center is the heart of a modern enterprise, providing computing, storage and networking resources necessary to support varied and demanding enterprise applications that drive the business. Traditionally, a business builds, equips and operates its own data center -- and might even support multiple data centers constructed in strategic regional or global locations. But traditional, full-featured data centers are complex and expensive constructions with finite resources. Sometimes a business simply can't afford to build, operate or expand such a capital-intensive investment. Rather than build and operate a private data center, a business can choose colocation, opting to rent or lease data center capacity offered by a remote colocation provider and access the colocation across a WAN, such as the internet.
Colocation is IT-focused and intended to provide some level of data center support to client businesses. At the lowest level, a colocation provider -- or simply a colo -- maintains and offers clients access to basic facilities, including physical building space, power, cooling, physical security and telco access for WAN support. Clients simply rent or lease space in the facility, but move in their own computing, storage, networking, other gear and personnel. This model eliminates the expense of building and operating a data center facility, though the client business owns and operates the IT equipment.
Colocation providers might go further by also hosting the computing, storage, networking, software tools and expertise needed to operate a complete data center. Such hosted or colocation providers offer complete platforms for client businesses in need of data center resources but that choose not to build or equip their own data center facilities. An ultimate expression of colocation is managed colocation, where the provider operates a fully equipped data center and simply rents access to provisioned resources, such as virtual machines, and even applications and services, such as backup services, running in the colocation facility.
Colocation providers can often be quite distant from the client business, making it challenging for the business to send IT personnel to work with gear located in the colocation facility. Travel is expensive and time-consuming, and might not be practical in an emergency situation when a service or system requires immediate attention. Providers frequently offer remote hands services, using the providers' IT personnel to conduct an array of services -- such as moving cables, changing gear configurations, cycling power and rebooting, removing or installing gear -- at the clients' request. Remote hands don't apply when the colocation provider owns and operates the gear -- that's just the provider's own IT team doing its job.
Why do businesses use colocation?
Colocation is attractive as an IT service because it helps businesses solve problems or achieve results that might be too expensive or complex for the business to accomplish by itself.
There are four principal drivers for adopting colocation: cost, performance, compliance and services.
Cost. A full-featured data center is expensive. A new data center can take years to build and cost a business tens of millions of dollars to construct the building, purchase and deploy gear and install WAN fiber -- not to mention yearly operating costs for electricity, maintenance and taxes. Even a business that makes the investment in one full data center is usually reluctant to afford a second. Thus, using a colocation provider can shift significant financial burden from the business. Consider some cost-driven uses for colocation:
- A business can minimize its local computing facility investment -- essentially avoiding a traditional data center in lieu of a vastly scaled back facility, such as a container data center, for the most mission-critical workloads and then using colocation for more routine, experimental or transient workloads and services.
- A business that already owns and operates a traditional data center can eliminate the need to build additional data centers, instead using colocation facilities for subsequent data center platforms in other geopolitical areas as business interests demand.
- Colocation facilities can be employed to replace an array of regional remote office/branch office IT deployments, effectively centralizing IT for busy ROBO demands. A centralized resource can be easier, more secure, more scalable and more efficient to manage and maintain than individual ROBO deployments.
Performance. Today, businesses require a global presence, but a global presence also means global access to applications and data. A single data center is hard-pressed to support the demands of global users. Even when a business makes the investment in costly network bandwidth, physical realities of network latency, congestion and connectivity can lower workload availability and performance for remote users -- potentially affecting user satisfaction and workload use. Colocation enables businesses to get workloads and data closer to users in different geographical regions to maintain adequate workload performance without the need to build new facilities.
Compliance. Global businesses also face increasing government regulatory demands that affect the way applications are used, and the way application data is managed and secured. A single data center might not satisfy the data residence requirements of some nations or other political and economic blocks. As with performance, colocation can help a business to satisfy prevailing regulatory requirements without the need to undertake additional large and costly constructions by engaging the colocation offerings of a provider already operating in the target geopolitical area.
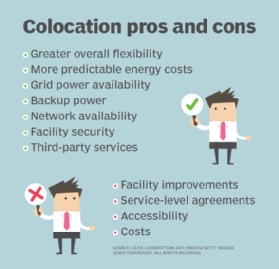
Services. Finally, a single traditional data center is a single-point-of-failure vulnerability for the business. Fires, earthquakes, floods and storms, and even man-made accidents or disasters, can bring connectivity and facilities disruptions -- to power and cooling, for example -- which can affect the availability of critical applications for all users. The best way to handle disaster recovery is through redundancy. Colocation is a cost-effective and logistically efficient means of building DR redundancy in critical workloads. The colocation facility can be used as a warm site -- effectively a backup or standby site. But it can also be a hot site that carries part of the application's compute load.
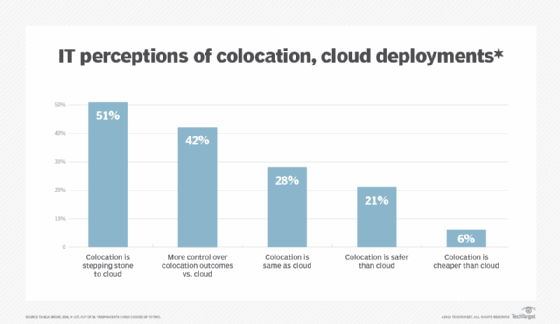
The emergence of cloud computing has brought some confusion to colocation. Cloud computing and colocation are increasingly used interchangeably, though this is entirely incorrect. Cloud computing offers many of the same use cases as colocation. The principal difference is the way the technologies are positioned. A cloud is designed to offer IT resources and services that are entirely managed by users but owned and operated by the cloud provider -- the cloud is computing as a utility. Colocation has a far more traditional bent, offering physical facilities and resources that client businesses can employ for their own purposes. It's possible to operate a private cloud in a colocation data center, where the cloud software stack can be deployed to gear architected to support the cloud stack, and IT administrators can craft the varied private cloud services needed by the business. It's not possible to operate a colocation business from a cloud.
The benefits and drawbacks of colocation data centers
Colocation works because it fundamentally provides a client business with a cost-effective remote computing presence in politically or geographically strategic locations without needing to build and equip a physical facility. The facility -- and often its computing resources -- is already supplied by the colocation provider and can be used for myriad purposes.
However, there are numerous pros and cons involved with colocation that every business should carefully evaluate before making a colocation commitment. Beyond the beneficial issues of cost, performance, compliance and services, there are several additional colocation benefits to consider:
- Costs are largely inclusive. Colocation costs are primarily recurring operating expenses that cover the provider's costs and profit. The power distribution, cooling, security, connectivity, maintenance and other costs of running the colocation are all included in the recurring fee paid by the client business. Additional costs might be incurred during initial setup and through changes, updates and additional connectivity options.
- Useful services might be available. A colocation provider might have thousands of clients present in many interconnected colocation data center facilities around the world. Many clients offer useful services such as SaaS or microservices, and those services can be contracted and used at data center speeds -- those businesses are essentially operating within the same network of high-speed data centers.
- Scalability can be negotiated. A traditional data center is a fixed asset, but an organization's computing needs can change over time. This might leave the traditional data center underutilized or pushed beyond its capacity. Colocation eases this problem, and contracts can be renegotiated to add or remove space or gear as needs change. A business can engage a colocation provider for current needs and then change those needs over time.
- Colocation can be more resilient. Availability and resiliency are critical factors for colocation providers that can have hundreds of clients in a single facility -- a power or cooling failure would be catastrophic for the colocation provider's business. Thus, it's common for colocation facilities to invest heavily in resilient infrastructure that can then benefit the provider's clients.
Although there are appealing benefits to colocation, there are also common drawbacks that affect client businesses and their ability to work with the colocation provider. Typical pitfalls include the following:
- Access is limited. Remember that the colocation facility is a separate business, and there are strict limitations to access. Although equipment management and monitoring can usually be accomplished remotely, physical access -- such as adding, removing, repairing or reconfiguring gear -- is tightly controlled. If the colocation provider owns and provides the gear, the client business might not have access.
- Travel can be costly. Sending technicians to remote colocation sites to work with client-owned gear can become an expensive proposition. Remote hands services offered by many colocation providers can help alleviate time and travel costs, but such services can carry additional costs.
- Cost factors differ. Although colocation carries recurring costs, the factors that determine those costs can differ by provider. Providers might use different formulas that involve power used, space rented and other variables to calculate fees. These differences can make it difficult to compare colocation provider costs directly.
- Contracts can constrain. Colocation usually carries long-term contracts that lock businesses into the provider for several years. This can be problematic if costs fall, business needs change or other terms become unsuitable for the client business. Contract terms might curtail re-negotiation, so contracts must be examined and evaluated carefully.
- SLAs are hard to verify. The center of any colocation agreement is the service-level agreement, but monitoring and enforcing the SLA is fraught with problems. It's vital for a client business to investigate monitoring and reporting, validate interoperability between client systems and provider tools and be able to measure and verify remediation targets -- such as time to remediate an outage. Otherwise, there is no valid means of enforcing an SLA.
- Facility lifecycles vary. Today's state of the art data center might be obsolete in just a few years, so the biggest challenges for a data center is staying up to date and fit for purpose. Investigate the colocation provider's maintenance and upgrade roadmap and see how older facilities have been upgraded over time.
What are the challenges of moving to a colocation data center?
Making the move to a colocation provider might seem straightforward, but the process of adoption is rarely quick or easy. Although the initial investment is far less than a new data center, it's a business decision that must be approached cautiously because colocation agreements pose long-term commitments and constraints. Client businesses must perform extensive due diligence to select the most appropriate colocation provider, site and terms to fit current and future business needs. Here are some common challenges to consider:
- Response times. When a problem arises in a local data center, the business leads the charge to fix it; staff, resources and tools are all available and dedicated to the business' needs. A business that owns the data center effectively owns the availability and response time. A colocation provider is basically a business partner with troubleshooting priorities and response time goals that may differ substantially from those of a client business. Colocation clients must think about how to troubleshoot and restart applications and servers when there are outages. Remote hands services can help, but fixing problems will inevitably take longer and is always governed by the colocation provider's SLA. Providers might require a formal trouble ticket and escalation process, which can also lengthen the response time. Long response times can affect the type and criticality of workloads deployed to a colocation partner.
- Scalability. Any colocation provider is happy to rent more space and resources, but the offerings are finite, and there is typically a lag of weeks -- perhaps months -- before changes to the colocation contract can be negotiated. There might also be a limit to the number of changes that can be implemented in a period of time. This is radically different than public clouds where resources can be added, used and retired in minutes.
- Transparency. Modern businesses must see what's happening in the data center. Technical and procedural transparency is essential to ensure the health and availability of client workloads, provider adherence to the SLA and even to validate client security and regulatory compliance. But a colocation provider can be distant, making them costly and time-consuming to reach. Access to the facility might be limited or even prohibited if the client is renting servers, storage and other gear. And remote management tools might not fully integrate with local infrastructure or provide a complete picture of the provider's environment.
- Noisy neighbors. Unlike public clouds, which are based on shared resources, colocation facilities typically don't share resources other than facility-wide power, cooling and other physical functionality. The servers, storage and other gear are typically racked and caged for the exclusive use of the respective client. However, there are inevitably shared resources, including LAN and WAN access. When network resources are shared, the potential for noisy neighbors exists -- potentially affecting the performance of critical applications. Client businesses should monitor workload performance carefully and identify performance disruptions for prompt remediation by the colocation provider.
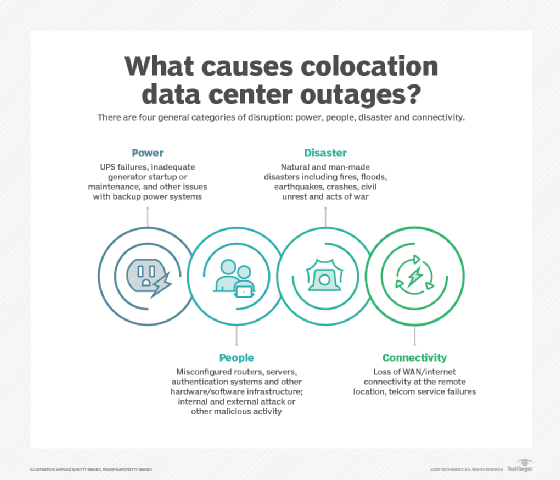
Comparing types of collocated data centers
Colocation providers are frequently classified as wholesale, retail or hybrid. The three terms generally denote the scale of the colocation offering and the client market for which it is intended.
In the world of physical goods, buying wholesale typically means buying in volume -- but at a sometimes-considerable cost savings. A wholesale colo basically offers a fully provisioned and equipped facility for the dedicated use of a client business. In effect, the client rents the entire colo -- or a significant portion of the overall facility -- which includes the maintenance, power distribution, connectivity, uninterruptible power supplies, auxiliary generators, fire suppression and other elements of a full-featured data center.
Wholesale colocation only makes sense for the largest businesses where IT equipment would require 1 megawatt or more. Wholesale can be a suitable option for large businesses that require a significant IT presence in a strategic location but opt not to make the investment in constructing or maintaining a building -- for financial, legal or other reasons. For example, a large U.S. business might prefer to rent a wholesale colo in Asia for AMEA operations rather than undertake the financing, permitting and other regulatory challenges of building and owning a major asset in another country.
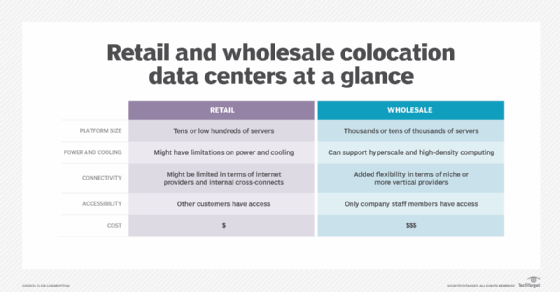
In terms of physical goods, buying retail means buying in small quantities through stores or other distribution means. The buyer can pick and choose much smaller quantities as needed, but the cost of the goods is typically higher because of the additional distribution network involved. A retail colo allows a client business to rent space and gear as needed, often allowing the client to place its own equipment in racks within the facility.
Retail colocation offers flexibility and cost management, and the facility expenses are shared across the entire client base. This makes retail colocation preferred for most small to midsize clients, but the retail space is shared -- not dedicated -- and some means of partitioning and securing the facility are critical.
Hybrid colocation typically involves a mix of managed retail colocation and cloud interoperability. The idea is that a client business might choose to embrace managed, software-defined colocation and then use public and private cloud capabilities that are facilitated by the colocation provider, essentially using the colocation provider as an on-ramp to cloud computing.
What to look for in a colocation provider
Planning and research are essential to successful colocation initiatives. The stakes can be high. A typical retail colocation contract can last from three to five years, while a wholesale colocation agreement can run from five to 15 years. Even short-term contracts can be devastating for businesses that pick inadequate colocation partners, so due diligence can help client businesses determine the best provider for their unique needs now and well into the future. Common considerations when selecting a colocation provider include the following:
- Power density. Understand how much power -- in kilowatts or even megawatts -- the colocation provider can deliver, and discuss the power and cooling requirements clearly. Many colocation providers were designed for about 5 kW per rack and struggle to support 10 kW per rack. With today's high-density technologies, such as HCI demanding significant power and cooling for high-density blade enclosures, power and cooling limitations might result in a significant power surcharge and could knock a colocation candidate off the list.
- Floor space. Think about rack consolidation and floor space costs. Renting more space at a colo doesn't improve performance or resilience, so minimizing the floor space requirements for a colo deployment can save significant costs over the life of the contract. Many businesses manage rack power density, cooling and floor weight distribution by reducing -- spacing out -- the servers and other racked gear. If the colocation provider can accommodate the added power and cooling density of full or taller racks, a client business can potentially fit more gear into a smaller data center footprint.
- WAN redundancy. A colocation provider should be carrier neutral and include connectivity to varied network carriers at the facility. Client businesses pay a separate fee for network connectivity -- telco costs aren't the responsibility of the colocation provider. A colocation provider hosting a wide variety of network carriers can bring competitive WAN pricing for client businesses and allows for redundant client connectivity.
- Contract and SLA flexibility. Obtain and review the prospective provider's primary service agreement and SLA right away and review the documents with legal, business and IT teams to address contract items that are mission-critical -- such as availability, response times and scalability. Discuss concerns with the prospective provider and see if the provider is willing to negotiate better terms. If not, the provider might not be appropriate for the business.
- Location. Decide where the colocation site should be, and why it needs to be there. If the site is strictly for DR, it should be within about 100 miles of the main business -- but far enough away to guard against the fire, flood, hurricane or other threats that drive the need for a DR site in the first place. Similarly, if the goal is to improve global presence, consider the target market and see that the provider offers suitable facilities to serve that marketplace. Location affects accessibility, and remote sites might require remote hands or other management platforms when IT staff can't easily reach the site.
- Compliance. Verify that the colocation provider meets -- complies with -- the certifications or industry-recognized data center tier levels that the provider claims. For example, colocation providers might embrace Tier availability as certified by the Uptime Institute, a class system used by the ISO or a level system used by the Telecommunication Industry Association. Regardless of the provider's certification claims, it should be able to verify its certification and allow third-party audits for validation. Such validation might be vital for the client's own regulatory or industry compliance in operating certain workloads.
- Security. Colocation providers typically offer stringent physical security, but review the provider's security measures, ensure those measures are suitable and discuss options for adding more security measures -- such as client cameras within the rented floor space -- if desired.
- Services. Even the most basic colocation provider should have local staff and a menu of some fundamental managed services available. Services can help support clients with vital -- albeit routine -- tasks, such as backup and DR planning/testing. Or the provider can offer remote hands to help manage and maintain equipment without the need to send local IT staff each time a server needs rebooting or a network cable must be moved. Today, providers rely on a rich ecosystem of vendors and partners for services.
- Roadmap. Think ahead. Colocation success often requires a long-term alignment between the provider and client business. Discuss future plans, see where the colocation provider is going, let them know where the business will be heading and be sure that any contracts will allow for changes over time. For example, if the client will need more services over the term of the contract, but the provider has no plans to add such services, that provider might not be the right fit for the business.
Colocation cost and pricing considerations
Colocation providers can vary radically in their offerings and services. Clients can lease huge bare-bones, empty data center space or rent servers and other resources that are owned and managed by the providers. Clients can do everything themselves or use an array of potential services offered by a provider. Such a diverse array of choices make uniform cost comparisons between providers almost impossible, but there are cost and pricing considerations that can help business leaders avoid costly mistakes in colocation selection.
Facility vs. managed. Leasing space in an empty data center colo isn't necessarily cheaper than renting capacity from a managed colocation provider. Leasing a facility will typically work on a square footage or square meter basis and will often include finite power and cooling per rack. Power and cooling demands beyond the provider's default capacity might carry a power and cooling surcharge. Still, the business must purchase gear, move it into the facility and then deploy, configure, test and maintain the gear. Some colocation providers might also be able to rent gear to the client. Gear rentals carry additional costs, but the DIY model remains.

Alternatively, a business can adopt hosted colocation that includes the gear and might also include some OS licenses -- though software licenses are often options. In this case, the provider owns the building and gear and the business is simply renting servers or racks. Costs are typically expressed in terms of fractional racks, or U space. For example, a managed colo might rent a full rack -- 42U -- for a given monthly cost. Managed colocation is similar; however, costs might be further divided into virtual machines on shared or multi-tenant servers -- unless the clients are renting entire servers in a single-tenant mode.
Power. Power might be included with default colocation pricing, but there can be power surcharges for usage over the default amount. Some providers might employ separate power billing methods, such as per kilovolt ampere or a metered amount for the actual power used. Redundant -- A/B -- power might be included by default, but it might also be offered as an option that incurs extra costs. If power usage is expected to increase dramatically over the life of the contract, let the provider know, and it might be possible to arrange stepped power pricing for the contract term.
Services. Colocation typically doesn't include services. Whether a DIY space or managed colocation, it's usually up to the client business to deploy gear or use provisioned servers and VMs. Providers might offer deployment and setup -- a.k.a. rack and stack -- services that can be cost-effective if there aren't enough staff to send to the colo or the cost of setup exceeds the cost of the provider's services. This is usually a one-time setup fee. Other services include remote hands, which usually carry a billable hourly charge.
Connectivity. The colocation facility will typically provide accommodation for multiple telecom providers, but selecting bandwidth offerings and connecting to a preferred provider is usually a task handled by the client, with additional connection and connectivity costs shouldered by client businesses. Connectivity costs might be rolled into a hosted or managed colocation agreement, though redundant connectivity might carry additional recurring fees for more than one telecom provider. Colocation providers are increasingly offering transitional services to public clouds and can extend some amount of public cloud infrastructure into the colocation facility. One example is AWS Direct Connect, which enables the colocation provider to provide high-speed connectivity to the AWS cloud.
Location. The quintessential rule of all real estate is location, location, location. More desirable locations, such as urban centers and sites close to major infrastructure such as airports and multiple highway interchanges, might carry a premium cost for real estate. These sites also tend to offer more connectivity options at lower costs. Remote sites farther from transport and other infrastructure can offer less expensive real estate but pose more expensive transportation costs. The cost of a colocation provider should justify the reasons for having it.
Consider the need for other location amenities such local parking, office space, meeting rooms and food and beverage services. Not all colocation facilities provide amenities, and some might charge for certain ones. For example, a colocation site in a major city might charge for parking and have challenges loading and unloading, while a remote site might offer plenty of free parking and readily accessible loading and unloading.
Hidden fees. Read the fine print. Although major fees, such as leasing and power costs, are readily understandable, many other fees might be more difficult to see -- such as setup and change fees, redundant power or other availability features, backup and data protection services and network bandwidth and connectivity fees. Review the primary service agreement and SLA carefully and look at service guarantees, including uptime guarantees. SLAs that rely on best effort and other nonspecific availability terms might pose significant costs in terms of downtime and lost business. Understand how SLAs are measured and be sure that such measurements are transparent and readily reported to clients.

Colocation contract negotiation
Colocation promises an array of compelling benefits, but choosing a provider can bring anxiety and new concerns to the business. Unlike public cloud computing, which uses a pay-as-you-go model, colocation requires a contract that can lock clients into a colo relationship for years. Choosing the right provider and understanding the many details and exceptions to the relationship can make the difference between success and failure.
The relationship between a colocation provider and its clients is governed by the SLA. Understanding the SLA and negotiating the SLA terms to suit the client's specific needs are key to a successful colocation experience.
Clarity is the most effective tool for approaching an SLA. A client business should have a clear picture of why they need colocation and the benefits that such a relationship should provide before ever looking for a provider. If business and IT leaders know what's needed upfront, it's much easier to examine any contracts and agreements to ensure those needs are met, or frame discussions to address those needs. Basic due diligence is also crucial when considering a provider and SLA. Beyond the actual uptime promises for power, network, cooling and other equipment, take the time to evaluate factors such as the following:
- the provider's onsite support response times;
- telephone support response times and escalation policies;
- refund or credit policies for both planned and unplanned downtime;
- scaling or change policies;
- reporting and notification -- SLA adherence -- policies;
- root cause analysis for any downtime; and
- agreement or relationship termination clauses.
Now it's possible to compare the provider's offering to the businesses' needs, and businesses can move forward to negotiate the contract to address any unmet needs. If the provider can't address any outstanding contractual concerns, it's probably best to keep looking. No deal is better than a bad deal.
Once a satisfactory deal is struck and the relationship is proven, the contract will eventually come up for renegotiation and renewal. The renewal process typically involves extending the contract term, adjusting the colocation space or gear, making changes to any contract deficiencies and considering other available value-added services that the provider might offer. Thus, renewal should start long before the current contract expires, with the client considering changing needs and goals. Those client-side changes can then be brought into the renegotiation discussion. Clients can also consider cost-saving strategies such as re-racking gear to reduce floor space and extending contract terms for longer periods.
Still, even the most carefully negotiated agreements with the most accommodating colocation provider can end in disappointment with missed guarantees, rising costs and fees or poor performance. When the provider is unable or unwilling to resolve client concerns, it might be necessary to end the colocation relationship. But unless a client can make a solid case to invoke a termination clause of the contract, the result can be considerable contractual costs and even litigation.
Ending a colocation contract typically starts with a careful review of all agreements to verify the roles and responsibilities of both the colocation provider and the client. Document and detail every event or circumstance where the colocation provider is believed to be failing its contractual responsibilities. Outline every effort to address the problems and document those efforts with dates, times and persons involved. The goal is to bring the provider to the table to fix deficiencies or renegotiate the contract.
If the problems persist, it might be necessary to bring legal action with attorneys well-versed in technology service contract litigation. At this point, the goal is still the same: Get the provider to live up to its commitments under the colocation agreement.
Ultimately, it might be necessary to invoke a suitable termination clause under the prevailing colocation agreement and proceed to terminate the contract. This means an end to the current colocation relationship, and it will be necessary to find another provider. The time, effort and potential disruption involved for such a shift can be considerable, so it's important to exhaust other avenues of remediation before dumping the provider.
Colocation trends in 2021
The colocation industry continues to change and evolve, bringing new capacity and capability to meet enterprise computing needs. Several noteworthy colocation trends are emerging for 2021 and beyond.
Hosted and managed colocation is becoming more granular and flexible. Providers can readily rent as little as 1U -- a single server -- for short monthly terms, though long-term discounts will inevitably make longer commitments more attractive to clients.
Colocation is increasingly being used as an on-ramp to the public cloud, enabling traditional data center-based businesses to transition from local data centers to colocation data centers. Then they can easily transition workloads from the colocation data center to a public cloud and back for faster and more workload deployment alternatives.
Finally, colocation is supporting more specialized use cases, including distributed data networks, high-throughput data processing tasks and edge computing where moving compute power closer to data sources can speed performance and reduce latency.







