HVAC (heating, ventilation and air conditioning)
What is HVAC (heating, ventilation and air conditioning)?
HVAC stands for heating, ventilation and air conditioning. In computing and especially in enterprise data centers, HVAC systems control the ambient environment (temperature, humidity, air flow and air filtering) and must be planned for and operated along with other data center components such as computing hardware, cabling, data storage, fire protection, physical security systems and power.
Almost all IT hardware comes with environmental requirements that include acceptable temperature and humidity ranges. These requirements are usually described in product specifications or physical planning guides. A data center HVAC system must take into account all environmental requirements across the full spectrum of devices, along with applicable fire, safety, security and ecological concerns.
For this reason, an HVAC system must be carefully planned, implemented and maintained. It should also include disaster preparedness. For example, a data center might implement redundant HVAC components, keep spare parts on hand or maintain backup systems such as portable air conditioners.
What does HVAC encompass?
An HVAC system maintains a regulated temperature, controls the level of humidity and ensures optimal air quality. As the HVAC acronym indicates, the system includes the following components:
- Heating. An HVAC system includes some type of equipment -- such as furnace, boiler or heat pump -- for generating heat that is used to warm an internal space. The equipment might target a room, zone or entire building. Heating equipment uses different methods to heat a space (conduction, convection or radiation) and uses different types of resources to generate the heat, such as electricity, propane, heating oil or natural gas. Although heating is usually not the primary concern in data center HVAC, it's still an important factor, particularly in cold climates, where heat might be needed to protect outdoor equipment or components such as chillers.
- Ventilation. A comprehensive system of ventilation is essential to effective HVAC. Ventilation is a separate mechanism from heating or air conditioning but works in conjunction with both, maintaining the airflow necessary to effectively heat or cool a building. In addition, it exchanges inside air with outside air to ensure a fresh supply. Ventilation can also play a role in filtering the air or maintaining the proper level of humidity, depending on the heating or cooling system. Proper ventilation is especially important in data centers, where it's used in concert with air conditioning to cool IT infrastructure. Data centers employ a variety of strategies to ventilate and cool their systems, depending on the type of equipment and their layout.
- Air conditioning. An HVAC system includes some type of equipment to cool circulating air. The approach to cooling can vary significantly from one commercial space to the next. For example, air conditioning equipment might be located inside the building or on the outside, such as on the roof. It might also use water to control temperatures, rather than coolant. In addition, it might play a role in filtering the air or controlling humidity, working in conjunction with the ventilation system. Data centers rely heavily on air conditioning to ensure that IT infrastructure can operate properly, using a variety of strategies to cool and ventilate their systems.
Although HVAC components are independent systems, they operate as an integrated whole whose goal is to properly control and maintain the climate of an indoor space. In recent years, commercial HVAC systems have started to become more automated and more intelligent, incorporating advanced technologies such as machine learning, deep learning and predictive analytics.
HVAC vs. air conditioning
Discussions around HVAC often raise the question: What is the difference between air conditioning and HVAC? However, it would be better to ask how air conditioning fits into the larger HVAC system.
Air conditioning should be thought of as an integral component of HVAC, along with heating and ventilation, rather than something different from HVAC. Air conditioning works hand-in-hand with ventilation to cool the circulating air, just like heating works hand-in-hand with ventilation to warm the air.
Some data center HVAC systems incorporate plenums into their designs. A plenum is a dedicated space for circulating air and is typically located under a raised floor or between the structural ceiling and a drop-down ceiling. In some cases, the plenum also houses communication cables. If so, the cables must be rated for the plenum environment. Plenum-rated cables are more fire resistant and emit fewer toxic fumes than regular cables.
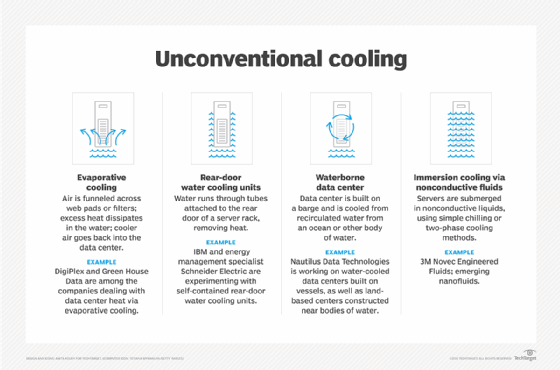
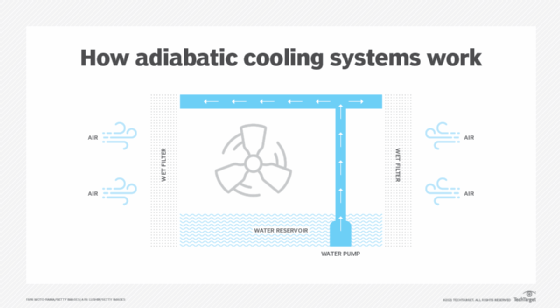
See also adiabatic cooling, free cooling and liquid immersion cooling. Learn about unlocking the benefits of a smart building , what a data center facility manager does and green computing best practices.







